
Als Wir Uns Das Erste Mal Song
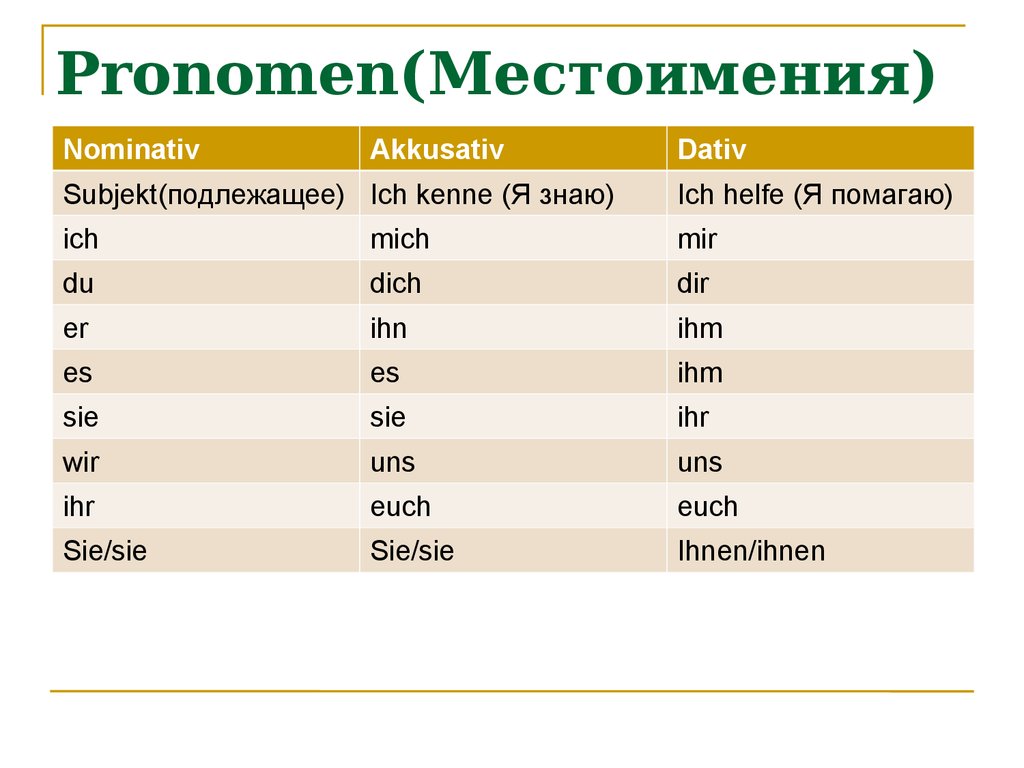
ich liebe dich = je t. mich: mir: du: dich: dir: er/sie/es : sich: sich: wir : uns: uns: ihr: euch: euch: Sie: sich: sich: sie: sich: sich . Exemple d'accusatif; ich wasche mich = je me lave. Exemple de datif; ich putze mir die Zähne = je me brosse les dents Recevez le guide gratuit Les 100 verbes les plus utiles en allemand En vous.

Reflexive Verben, German Language Learning, Development, Art, Grammar, Deutsch, Quotes, Art
Reflexive pronouns (myself, yourself, etc) are more common in German than in English, because there are many more verbs that require them. (Reflexive verbs will be covered in Section V.12 .) By default, a reflexive pronoun is the direct or indirect object of a verb, so it can only take the accusative or dative case.
"mich, dich" 和 "sich" 和有什么不一样? HiNative
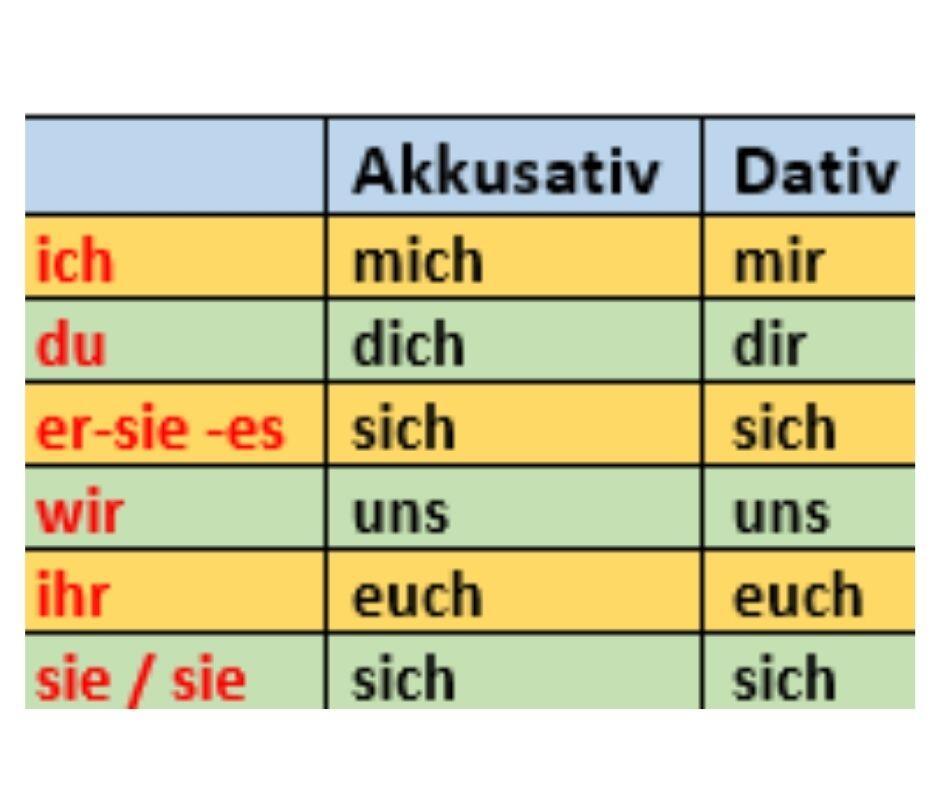
Reflexivpronomen sind mich, mir, dich, dir, sich, uns, euch und sich. Sie werden mit reflexiven und reziproken Verben benutzt. Sie beziehen sich immer auf das Subjekt. Beispiel: „Ich wasche mir die Hände." „Wir treffen uns." Bildung . Reflexivpronomen richten sich nach dem Subjekt und müssen dekliniert werden:

Reflexive Verben mich, dich, sich, mir, dir Learn German in Hindi/Urdu Level B1 YouTube
Reflexivpronomen werden auch rückbezügliche Fürwörter genannt. Die Reflexivpronomen im Deutschen sind: mich, mir, dich, dir, sich, uns, euch und sich. Ihre Funktion besteht darin, sich auf das Subjekt in einem Satz zu beziehen - sie beschreiben also Nomen näher. Reflexivpronomen können dekliniert werden. Das bedeutet, dass sie je nach.
Grammatik презентация онлайн
Note that only in the "ich" and "du" forms do reflexive pronouns differ in the accusative and dative cases (mich, mir; dich, dir).Only in the "er / sie / es" and "sie / Sie" forms do the reflexive pronouns (sich) differ from the normal personal pronouns (ihn, ihm; sie, ihr; sie, ihnen; Sie, Ihnen).3.
REFLEXİVPRONOMEN DEUTSCH DEUTSCHE GRAMMATİK
sich langweilen — to be bored sich umsehen — to look around sich verlaufen / verfahren — to get lost / go the wrong way (on foot/ by car) sich verspäten — to be late. Examples: Ich ruhe mich jeden Sonntag aus (I rest / relax every Sunday). Du sollst dich beeilen! (You should hurry!) Er hat sich schlecht benommen (He behaved himself.

deutschlernen pronomen michmir Objektpronomen Akk mich, dich, ihn, sie, es, uns, euch, sie
The reflexive pronouns (Reflexivpronomen) in German grammar are: mich/mir, dich/dir, uns, euch and sich. We use them with reflexive and reciprocal verbs. Reflexive pronouns always refer to the subject and must be declined to match the case they are in. Learn how and when to use reflexive pronouns with Lingolia, then practise everything in the.

erganze die satze mich dich sich uns euch Brainly.pl
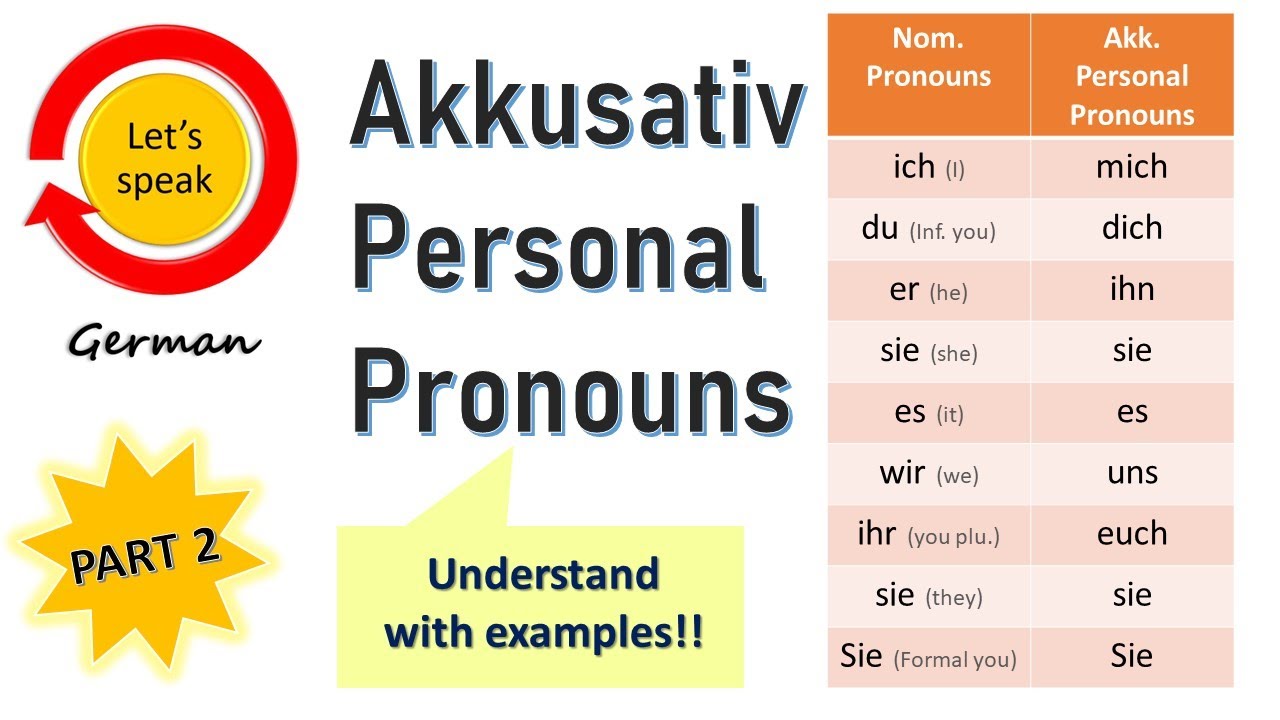
Both "me" and "you" have each two translations in German. "Me" can mean either mich or mir and "you" can mean either dich or dir. The difference between these forms is their grammar case. Mir and dir are DATIVE personal pronouns and mich and dich are ACCUSATIVE personal pronouns. Which grammar case we have to use in a sentence.

Reflexivpronomen, reflexive Verben, mich mir, dich dir, sich, uns euch, ihm, ihr, ihn ihm, ihnen
German pronouns. German pronouns are German words that function as pronouns. As with pronouns in other languages, they are frequently employed as the subject or object of a clause, acting as substitutes for nouns or noun phrases, but are also used in relative clauses to relate the main clause to a subordinate one.
Akkusativ PART 2 Personalpronomen (mich, dich, uns) German cases Grammar Lesson 9 A1
Rule 1: Some verbs are always reflexive, which means, we can't use them without a reflexive pronoun (mich/mir, dich/dir sich,.). The infinitive of these reflexive verbs is preceded by the pronoun "sich": German. English. sich befinden. to be located. German. English. sich beeilen. to hurry.

Mich oder mir gewöhnen, angewöhnen, abgewöhnen, umgewöhnen?
Les pronoms réfléchis allemands sont mich/mir, dich/dir, uns, euch, sich. Ils sont employés avec les verbes pronominaux. Ils se réfèrent toujours au sujet et sont de la même personne que celui-ci. Les pronoms réfléchis ne sont déclinés qu'à l'accusatif et au datif. Seules les 1 re et 2 e personnes du singulier sont différentes à.

Image result for mich dich mir dir German language, Learn german, German language learning
German reflexive verbs consist of two parts: the reflexive pronoun sich (meaning himself, herself, itself, themselves or oneself) and the infinitive of the verb. The present tense forms of a reflexive verb work in just the same way as an ordinary verb, except that the reflexive pronoun is used as well.. Ich setze mich neben dich.

Was ist das? mich dich sich Flickr
Er stellt sich vor- he introduces himself. Er fragt sich- he asks himself. However there are some verbs that are reflexive in German but not English, so don't be confused if you can't always translate sich to himself/ herself/ itself. 2. [deleted] • 4 yr. ago. the verb necessitating sich is erinnern.
Personalpronomen im Akkusativ (mich, dich...) It's a Match
Reflexive verbs (Reflexiv Verben) are verbs that take a reflexive pronoun (mich, dich, sich, etc.). In the infinitive, they are preceded by sich. Example: sich rasieren to shave sich anziehen to get dressed. With a reflexive verb, the subject and the object are one and the same. Example: Tom rasiert sich jeden Tag. Tom shaves every day.

Sich, mich, dich, uns, euch рефлексивні дієслова YouTube
Max und Tarek erinnern sich an das Jubiläum. (The subject is identical to the accusative object.) Personal pronouns. Reflexive pronouns. mich dich ihn sie es. mich dich sich sich sich. uns euch sie Sie. uns euch sich sich . Dative: Nico is looking for a job. Tarek hopes that he finds a job soon: Tarek wünscht ihm viel Erfolg.

OMG D mich dich sich Flickr
Die Reflexivpronomen (rückbezügliche Fürwörter) in Deutsch sind mich, mir, dich, dir, sich, uns, euch und sich.Sie beziehen sich auf das Subjekt (Satzgegenstand) eines Satzes. Das heißt, ähnlich wie alle anderen Pronomen (Fürwörter), beschreiben auch Reflexivpronomen Nomen (Namenwörter) näher. Reflexivpronomen - Beispiele: Ich habe mich sehr gefreut.